
1. AAA overview
Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) servers play a central role in managing user access and ensuring the integrity of network resources within provider networks. AAA servers are positioned within the provider network infrastructure, one or more Data Centers. They typically reside in the core of the fixed and mobile network. This central placement allows them to oversee and control access across various network services and access technologies, including broadband internet, mobile data, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
Role of AAA Servers are summarized below:
- Authentication: The primary function of AAA servers is to authenticate users attempting to access network resources. This involves verifying the identity of the user, often through a combination of username/password, digital certificates, unique pin, calling station id, or other authentication methods. AAA servers ensure that only authorized users gain entry, preventing unauthorized access.
- Authorization: Once a user is authenticated, AAA servers determine what actions or resources the user is allowed to access. This involves applying policies and permissions associated with the user’s identity, role, or subscription plan. For example, an AAA server might grant different levels of access to residential and business customers.
- Accounting: AAA servers also track and record user activities, creating a detailed record for each session. This accounting information is vital for billing purposes, troubleshooting network issues, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. It records the duration of sessions, data usage, and other relevant data.
- Policy Enforcement: AAA servers enforce network policies and quality of service (QoS) parameters. They can apply bandwidth limits, prioritize certain types of traffic, or restrict access during specific times. This ensures fair resource allocation and optimal network performance.
- Scalability: As provider networks grow, AAA servers must be scalable to handle increasing user volumes and traffic loads. They should also support redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure high availability.
In provider networks, AAA servers serve as the gatekeepers that control access to valuable network resources while ensuring the security, accountability, and quality of service. Their strategic positioning within the network infrastructure, coupled with their multifaceted role in authentication, authorization, and accounting, makes them indispensable components for delivering reliable and secure telecommunications services. As the demand for connectivity continues to grow, the importance of AAA servers in provider networks will only become more significant.
2. OpenProvider system modules
Current OpenProvider consists of three different modules:
- Policy and Charging Control (AAA – Authentication, Authorization and Accounting) – This is a module that enables the identification of Internet users, granting access, assigning appropriate policies, controlling access and user privileges. Finally, the system stores access data for further processing.
- Subscriber and Profile Repository – This module provides a domain and subscriber definition as mandatory, profile definitions (one or more) for the subscriber for each service the subscriber has and time-based or volume-based quota information.
- WiFi Captive Portals Management System – This module manage WiFi location and offer a possibility to set different policy rules for different locations. Together with captive portals this system also allows creating landing page per location or group of locations and present different content depending of age and gender.
Policy and Charging Control component of OpenProvider is based on two protocols:
- RADIUS protocol for access technologies such as copper, FTTx, 3G, 4G, WiFi
- Diameter protocol for interfaces that cover all PCRF functionalities. Currently, OpenProvider can support Gx, Gy, Gz, Sp and Rx interfaces for PCRF. The same Diameter nodes can support interfaces necessary for Voice over WiFi (VoWiFi) Diameter interfaces supported by OpenProvider for VoWiFi service are SWx, SWm and S6b.
The idea is to offer to clients one convergent system for all types of access technologies in the domain of AAA functionalities.
Subscriber and Profile Repository Component of OpenProvider is based on two protocols:
- LDAP protocol for fetching domain, subscriber, profile and credit information.
- REST protocol for integration with provisioning and various IT systems
OpenProvider consists of four VNFC components:
- Policing VNFC
- SSDB VNFC
- LDAP VNFC
- Apps VNFC

Policing VNFC has RADIUS protocol and communicate with NAS servers like BRAS, BNG, iWAG, EPG depending of access technology. Also Policing VNFC provide Diameter protocol with interfaces neccessary for PCRF and Voice over WiFi service. These nodes store in-memory OpenFunction and complete SME mechanism for handling incoming RADIUS and Diameter requests.
LDAP VNFC assume nodes with the LDAP protocol with full CRUD LDAP operations. It can be integrated with Policing VNFC with OpenProvider as well as other network components which has to get subscriber, profile and credit information.
Apps VNFC assume nodes with web application which we use for configuration of policy rules, NAS servers, adding dynamic IPv4 and IPv6 addresses pools, etc. This interface have dashboard with all statistical information on 1 minute resolution (number of request and response divided on response codes, QoS parameters, number of thread, number of TPSs..). This interface uses technical support because it has option to search active sessions, terminated sessions, service and system logs. Apps nodes work on HTTP(S) and support REST API for all data that platform poses. The same APPS nodes are usually used both for Policy and Charging Components and Subscriber and Profile Repository. This mean that domain, subscriber and profile provisioning is done via APPS nodes as well as credit and quota setting.
SSDB VNFC assume SSDB nodes that are the only statefull nodes. We use Cassandra cluster and this cluster keep all data for administration interface which mean that all active sessions will be here, terminated sessions, statistical data, policing logic etc.. The minimal deployment assumes 3 DC nodes and replication factor 3 because of redundancy and LOCAL_QUORUM consistency.
Beside there VNFC, part of the system is also VNF Manager. We use puppet as a software configuration management tool. Puppetmaster poses are necessary modules for complete project and one manifest for complete project. VNFM is also a rpm repository with all rpms for OpenProvider.
OpenProvider is located in at least two DCs as single VNF deployment. At least three physical servers should be available for OpenProvider VNF deployment on each site. VNF design and VNF components will be deployed providing both Local Redundancy (High-Availability on each DC), and Geo Redundancy (High-Availability across multiple DCs).
In order to prevent single point of failure within one DC, two same logical components must be on different availability zones or physical hosts.
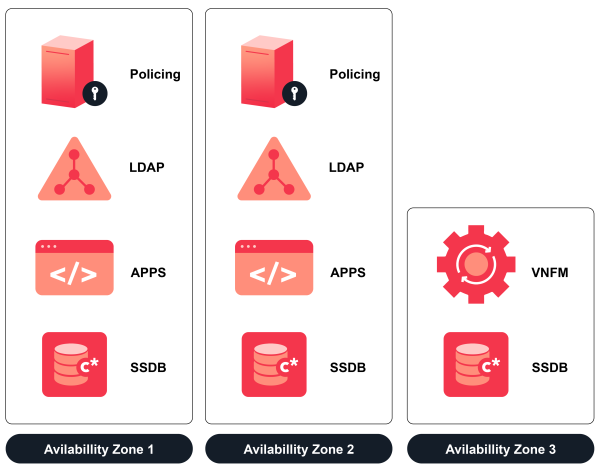
Minimal deployment includes:
- Two Policing nodes per DC
- Two LDAP nodes per DC
- Two APPS nodes per DC
- Three SSDB nodes per DC





